Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Analysis
Welcome to my blog on Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Analysis! Here you will find information about the differences between quantitative and qualitative data analysis and how to use them to make informed decisions. We’ll cover topics such as different types of quantitative and qualitative data analysis, the advantages and disadvantages of each data type, the benefits of combining the two, and the best software and tools used for both type of analysis.

Quantitative vs Qualitative Data
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Analysis
Types of Quantitative Data Analysis
Types of Qualitative Data Analysis
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative and Qualitative Data
Benefits of Combining the Quantitative and Qualitative Data
Best Software/Tools for Quantitative and Qualitative Data Analysis
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data
Quantitative data is numerical data that can be measured and compared numerically, while qualitative data is descriptive data that cannot be measured or compared numerically.
Quantitative data is used to quantify the characteristics of a population, such as the number of people in a certain age range, the average height of a group of people, or the percentage of people who are unemployed. On the other hand, qualitative data is used to describe the characteristics of a population, such as the types of jobs people have, their attitudes toward certain topics, or their preferences for certain products.
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data analysis is a process of analyzing numerical data, usually in a large dataset, to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. It involves the use of various statistical methods and statistical software packages. This type of analysis is also referred to as statistical analysis. Examples of quantitative data include population size, economic indicators, test scores, and sales figures.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of interpreting and understanding non-numerical data such as words, images, and videos. This type of analysis seeks to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. It is often used in a variety of social sciences such as psychology and sociology. Examples of qualitative data include interviews, surveys, focus groups, and observation.
Types of Quantitative Data Analysis
1. Descriptive Statistics: This type of analysis is used to summarize and describe data, such as mean, median, mode, range, and standard deviation.
2. Inferential Statistics: This type of analysis is used to draw conclusions based on data in order to make predictions or decisions. Examples include hypothesis testing, correlation, and regression analysis.
3. Exploratory Data Analysis: This type of analysis is used to explore data and identify patterns or relationships. Examples include principal component analysis, factor analysis, and cluster analysis.
4. Time Series Analysis: This type of analysis is used to analyze data over time in order to identify trends and seasonality. Examples include auto-regressive models, moving average models, and exponential smoothing.
5. Predictive Analytics: This type of analysis is used to make predictions about future outcomes based on past data. Examples include regression analysis, decision trees, and neural networks.
Types of Qualitative Data Analysis
1. Content Analysis: This type of analysis involves coding and categorizing data to identify meaningful patterns and themes. It is often used to analyze text-based data such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
2. Categorical Analysis: This type of analysis involves grouping data into distinct categories and then analyzing the differences between these groups. It is typically used to identify relationships between different types of data.
3. Narrative Analysis: This type of analysis involves analyzing the stories told by participants in order to gain insight into their experiences. It is often used to gain a better understanding of a particular issue or phenomenon.
4. Discourse Analysis: This type of analysis involves examining the way language is used to communicate ideas or convey meaning. It is often used to identify power dynamics or social norms within a given context.
5. Ethnography: This type of analysis involves studying a particular culture or group in order to gain a better understanding of their beliefs, values, and norms. It is often used to gain an insider’s perspective on a particular issue.
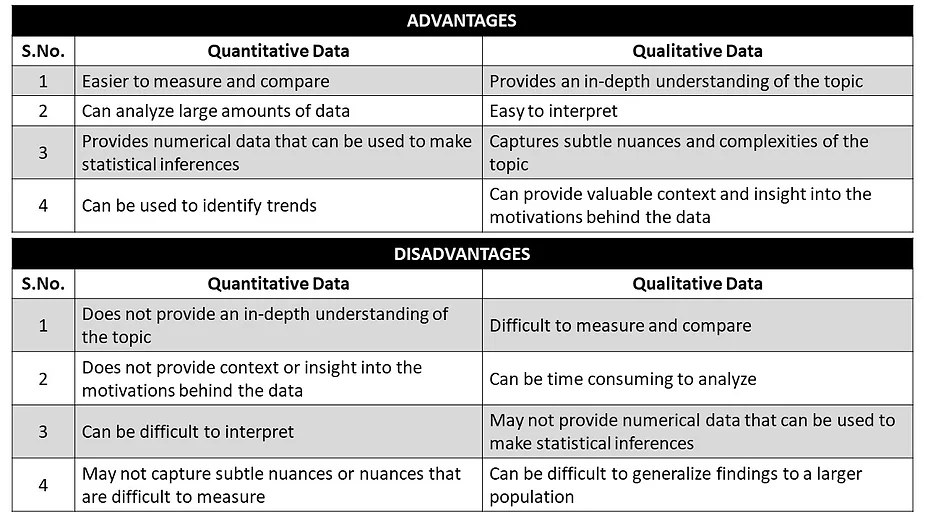
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative and Qualitative Data
Benefits of Combining the Quantitative and Qualitative Data
1. Improved accuracy and reliability: Combining quantitative and qualitative data can help to create a more comprehensive picture by providing more accurate and reliable results.
2. Broader scope of analysis: Combining the two types of data can provide a broader scope of analysis, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
3. Greater understanding of behavior: Qualitative data gives researchers a better understanding of how people think and feel about a certain topic. Combining qualitative and quantitative data can provide a more complete picture of the behavior of people.
4. Deeper insights into trends: Combining the two types of data can provide deeper insights into trends, allowing researchers to make more accurate predictions and decisions.
5. Better decision-making: Combining quantitative and qualitative data can help to create more reliable decisions, as it provides a more holistic view of the research topic.
Best Software/Tools for Quantitative and Qualitative Data Analysis
Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data analysis is an important part of data science and machine learning. There are many software and tools available to help with this task, but the best tools offer superior results and the most efficient workflow. Some of the top software and tools used for quantitative data analysis include SPSS, Tableau, R, MATLAB/Minitab, R, and Microsoft Excel,. These programs provide powerful features such as data manipulation, data visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning algorithms. Each of these tools provides something unique and has its own strengths and weaknesses. Ultimately, the best software and tools for quantitative data analysis depend on the needs of the user and the project they are working on.
1. SPSS: An industry-leading statistical software package used for data analysis and data management.
2. Tableau: A powerful data visualization and exploration software.
3. R: An open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
4. MATLAB/Minitab: A statistical software package used to analyze, visualize, and interpret data.
5. Microsoft Excel: Microsoft’s powerful spreadsheet program that simplifies data analysis.
Qualitative Data Analysis:
Qualitative data analysis is an important part of any research project. It involves analyzing data from a variety of sources, including interviews, surveys, observations, and texts. In order to make sense of this data, it is important to use the right software and tools. Fortunately, there are a variety of options available to choose from, including open-source and commercial software. The best software and tools for qualitative data analysis depend on the specific research goals, but some of the most popular options include NVivo, Atlas.ti, MAXQDA, Dedoose, and QDA Miner. Each of these tools provides a comprehensive set of features that makes them well-suited for analyzing qualitative data.
1. NVivo: A qualitative data analysis software used to analyze unstructured or semi-structured data such as interviews, open-ended surveys, and other qualitative sources.
2. Atlas.ti: A powerful qualitative data analysis software used to analyze and interpret text-based data.
3. MAXQDA: A comprehensive qualitative data analysis software that facilitates coding, text analysis, and visualization.
4. Dedoose: A web-based qualitative data analysis software that allows for the analysis of videos, images, audio files, and other media.
5. QDA Miner: A qualitative data analysis software used to analyze and interpret data from multiple sources.
We also discussed best practices for collecting, organizing, and interpreting data from both quantitative and qualitative sources. Click here to read more.
Thanks for taking the time to learn more about this important topic!




23 Comments
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/en-NG/register-person?ref=JHQQKNKN
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/id/register?ref=GJY4VW8W
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!